
COVID-19: Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms?. 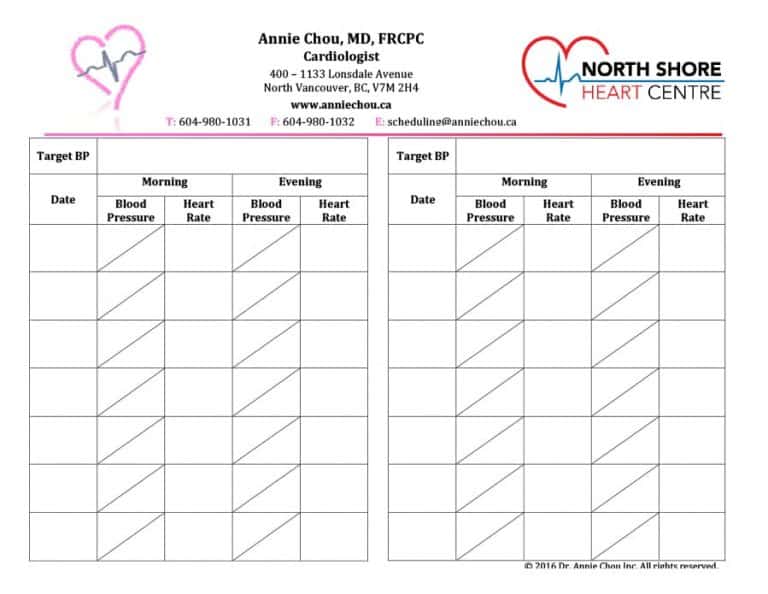 Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure?.
Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure?. 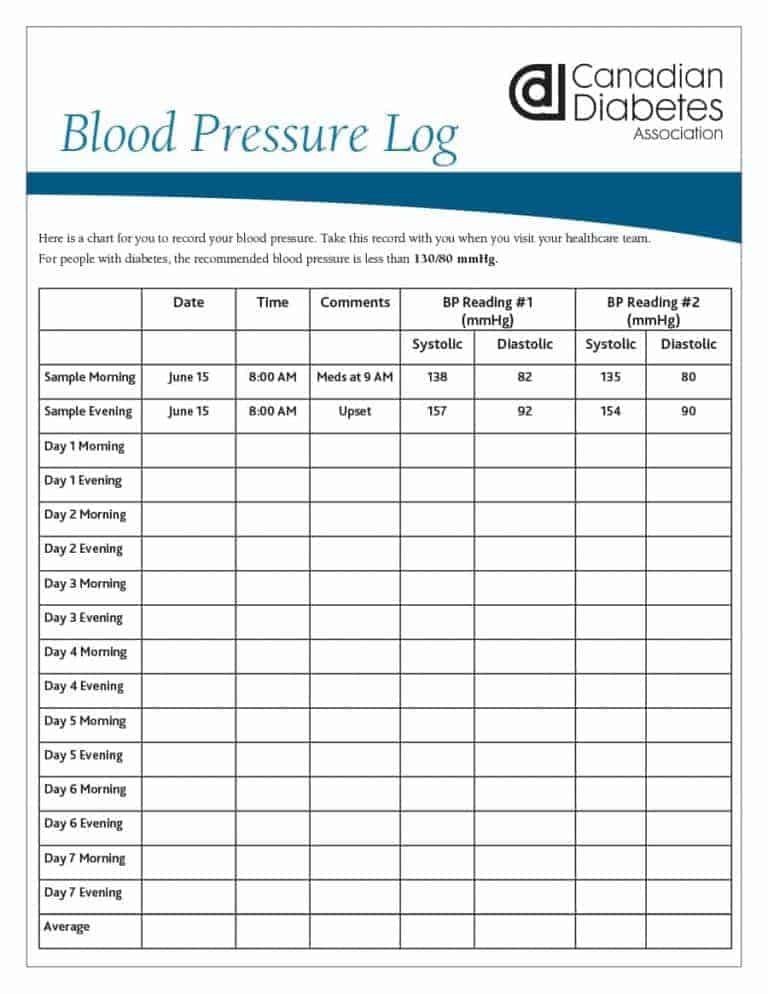 Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs?. Bump on the head: When is it a serious head injury?. Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes. Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons. Blood pressure tip: Know alcohol limits. Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home?. Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides?. Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight?. Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather?. Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm?. Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise?. Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain?. Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar?. Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure?. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure?. Impact of shift work on blood pressure among emergency medical services clinicians and related shift workers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Circadian mechanisms of 24-hour blood pressure regulation and patterning. Association of office and ambulatory blood pressure with mortality and cardiovascular outcomes. Journal of the American Heart Association. Development of predictive equations for nocturnal hypertension and nondipping systolic blood pressure. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in clinical practice. Impact of circadian blood pressure pattern on silent cerebral small vessel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Out-of-office blood pressure measurement: Ambulatory and self-measured blood pressure monitoring. It provides a detailed look at blood pressure changes over an average day and night. The test is called ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. This is called whitecoat hypertension.Ī 24-hour blood pressure monitoring test can be done to measure blood pressure at regular time periods over 24 hours. Sometimes, a person's blood pressure rises simply when seeing a care provider. Your health care provider can tell you if an irregular daily blood pressure pattern needs treatment. Not taking medications for blood pressure or sleep apnea as directed, or ineffective treatment. Poor diet, lack of exercise and certain lifestyle factors can affect blood pressure pattern, including: Less than 10% drop in blood pressure overnight (nondipping blood pressure)Ī rise in blood pressure overnight to early morning has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease.Īn irregular blood pressure pattern could also mean that you have:. High blood pressure early in the morning.
Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs?. Bump on the head: When is it a serious head injury?. Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes. Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons. Blood pressure tip: Know alcohol limits. Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home?. Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides?. Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight?. Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather?. Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm?. Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise?. Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain?. Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar?. Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure?. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure?. Impact of shift work on blood pressure among emergency medical services clinicians and related shift workers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Circadian mechanisms of 24-hour blood pressure regulation and patterning. Association of office and ambulatory blood pressure with mortality and cardiovascular outcomes. Journal of the American Heart Association. Development of predictive equations for nocturnal hypertension and nondipping systolic blood pressure. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in clinical practice. Impact of circadian blood pressure pattern on silent cerebral small vessel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Out-of-office blood pressure measurement: Ambulatory and self-measured blood pressure monitoring. It provides a detailed look at blood pressure changes over an average day and night. The test is called ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. This is called whitecoat hypertension.Ī 24-hour blood pressure monitoring test can be done to measure blood pressure at regular time periods over 24 hours. Sometimes, a person's blood pressure rises simply when seeing a care provider. Your health care provider can tell you if an irregular daily blood pressure pattern needs treatment. Not taking medications for blood pressure or sleep apnea as directed, or ineffective treatment. Poor diet, lack of exercise and certain lifestyle factors can affect blood pressure pattern, including: Less than 10% drop in blood pressure overnight (nondipping blood pressure)Ī rise in blood pressure overnight to early morning has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease.Īn irregular blood pressure pattern could also mean that you have:. High blood pressure early in the morning. 
Examples of an irregular blood pressure pattern include:










